Configuring the GPS2 CAN Output
To configure the GPS2 CAN output, click on the “CAN Configuration” button (highlighted in the image below).
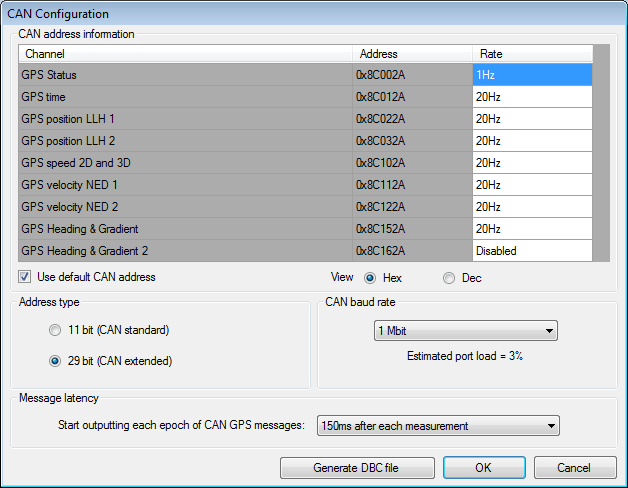
This will bring up the CAN configuration dialog as shown below.
CAN address information
Each CAN message that can be generated by the GPS2 is listed (for more detailed information on the format of each CAN message, please refer to the CAN message reference here). For each message, the CAN address can be independently configured, and the message rate can be set. The dialog will warn if any duplicate addresses are set, and will colour duplicates red to aid identification. The dialog will also calculate the approximate CAN bus loading as the message rates are set.
By ticking the box ‘Use default RT CAN addresses’, all addresses will be reset to the default values which work with the .dbc file available for download from the Race Technology website. This is recommended unless different CAN addresses are specifically required.
Addresses can be viewed in either hexadecimal (default) or decimal format. This is simply for the convenience of the configuration software user, and does not affect what is sent to the GPS2.
Address type
The CAN address type can be set to either 11 bit (CAN standard) or 29 bit (CAN extended) addressing. All messages share the same address type.
CAN baud rate.
The CAN baud rate can be set to either 125 kbit, 250 kbit, 500 kbit or 1 mbit per second.
Message Latency
CAN messages may be set to be output as soon as possible, in which case the latency is indeterminate, or they may be set to output with a fixed latency, which is 150ms after the relevant GPS epoch. The latency specification refers to the first message output for each epoch.
Generate DBC file
Clicking the "Generate DBC file" button will bring up a dialogue box which will enable the saving of a .dbc file which will work with all the listed messages using the addresses currently configured, regardless of whether each message is enabled or not. This enables the user to easily generate a custom .dbc file for their desired configuration.